A
AC adapter:
Mains adapter. Enables the connection of the digital camera to the main electricity supply.
ADC:
Analog-Digital Converter. Hardware that converts analog information into digital data. (>AD-Conversion)
Analog-Digital Converter. Hardware that converts analog information into digital data. (>AD-Conversion)
AD conversion:
Analog-Digital conversion. In order to process an analog signal (e.g. a photo) in a computer, it must first be digitized (converted into binary code). Pictures are usually digitized with the help of a digital camera or a scanner.
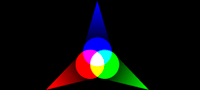
Additive color mixing:
Describes a colour system that is based upon the addition of the three additive primary colours (red, green, and blue).
For example, colour televisions and computer monitor displays use the principle of additive color mixing.
Describes a colour system that is based upon the addition of the three additive primary colours (red, green, and blue).
For example, colour televisions and computer monitor displays use the principle of additive color mixing.
Add-on /Add-in:
Extension to a program such as Excel or Word that increases the available functions. These add-ons/add-ins are developed and distributed by the respective software company or other firms.
Extension to a program such as Excel or Word that increases the available functions. These add-ons/add-ins are developed and distributed by the respective software company or other firms.
AE:
Automatic exposure.
A set of processing or working instructions that, because of their high precision, can be carried out independently by a mechanical or electronic device. Algorithms are, for example, the set rules for addition and subtraction etc. However, they are also the instructions that are established in a programming language. Algorithms simply allow the computer to solve particular problems. In image editing, algorithms are used to alter images, e.g. 3 D Cubic Algorithm.
Aliasing:
Pixel-shaped curves on the diagonal edges of objects. This can sometimes occur since all graphics consist of individual: pixels. Anti-aliasing reduces this unwelcome effect by recalculating the contrast values of the neighboring pixels and matching them up with each other.
Altavista:
Well known search engine in the internet.
Analog:
Opposite of Digital. Analog data merges continuously into each other without clearly defined steps (e.g. the colours of a rainbow are not obviously separable from one another).
Mechanism behind the lens that controls the amount of light entering the camera. The aperture not only influences picture brightness but also regulates depth of focus. Most cameras are equipped with an iris aperture that can be freely adjusted or set according to pre-selected values.
Apple Talk:
APS:
Advanced Photo System is a film format for still photography. Developed together by five companies, this film system is distinguished by simple operation, a new picture format (16 x 30 mm) as well as a choice of 3 picture formats. Additional information (such as exposure, aperture and date) can be recorded on the magnetic strip of the APS film.
Aqua Case:
Waterproof plastic casing for OLYMPUS CAMEDIA digital cameras.
The commonly used binary code for a total of 128 symbols (letters, numbers, punctuation and special symbols, however, not for umlauts) enables the correct data transfer between software and hardware. The ASCII-code employs the first seven bits of a byte. The first 32 symbols are used as control symbols, e.g. to control a printer.
ATA:
AT Attachment. Interface for harddrives.
AT Attachment. Interface for harddrives.
ATA Flash Cards:
Space-saving integtated plug-in memory cards.An Autofocus (AF) optical system uses a sensor, a control system and a motor to focus fully automatic or on a manual selected point or area.
There are basically two main AF methods: the focus detecting method, or passive auto focus usually employs a CCD and works by evaluating the amount of contrast or the phase difference in a scene. Distant metering or active autofocus utilizes an (infrared) light emitter and receiver in a triangular surveying system. Alternatively, the camera uses ultrasound (sonar) and measures the time taken for the sound signal to return. This data is converted by a microprocessor into information about distance and hereby enables the automatic focusing of the lens.
There are basically two main AF methods: the focus detecting method, or passive auto focus usually employs a CCD and works by evaluating the amount of contrast or the phase difference in a scene. Distant metering or active autofocus utilizes an (infrared) light emitter and receiver in a triangular surveying system. Alternatively, the camera uses ultrasound (sonar) and measures the time taken for the sound signal to return. This data is converted by a microprocessor into information about distance and hereby enables the automatic focusing of the lens.
A special exposure metering technique that measures the average light intensity across the entire frame.



















No comments:
Post a Comment